In the inherently information-driven insurance industry, companies ingest, analyze, and process massive amounts of data, requiring extensive decision-making. To manage this, they rely on a myriad of technologies and IT support staff to keep operations running smoothly but often lack effectiveness due to their outdated nature.
Artificial intelligence (AI) holds great promise for insurers by streamlining processes, enhancing decision-making, and improving customer experiences with significantly less time, resources, and staff compared with traditional IT systems.
The convergence of AI and innovative application datastores is transforming how insurers work with data. In this post, we’ll look at how these elements are reshaping the insurance industry and offering greater potential for AI-powered applications, with MongoDB at the heart of the converged AI and application datastore.
Scenario planning and flexible data layers
One of the primary concerns for IT leaders and decision-makers in the insurance industry is making smart technology investments. The goal is to consolidate existing technology portfolios, which often include a variety of systems like SQL Server, Oracle, and IBM IMS. Consolidation helps reduce inventory and prepare for the future. But what does future-proofing really look like?
Scenario planning is an effective strategy for future-proofing. This involves imagining different plausible futures and investing in the common elements that remain beneficial across all scenarios. For insurance companies, a crucial common thread is the data layer. By making data easier to work with, companies can ensure that their technology investments remain valuable regardless of how future scenarios unfold.
MongoDB’s flexible developer data platform offers a distinct architectural advantage by making data easier to work with, regardless of the cloud vendor or AI application in use. This flexibility is vital for preparing for disruptive future scenarios, whether they involve regulatory changes, market shifts, or technological advancements.
The role of AI and data in insurance
Generative AI is revolutionizing the insurance sector, offering new ways to manage and utilize data. According to Celent’s 2023 Technology Insight and Strategy Survey, 33% of companies across different industries have AI projects in planning, 29% in development, and 19% in production (shown in Figure 1 below). This indicates a significant shift towards AI-driven solutions by insurers actively experimenting with gen AI.
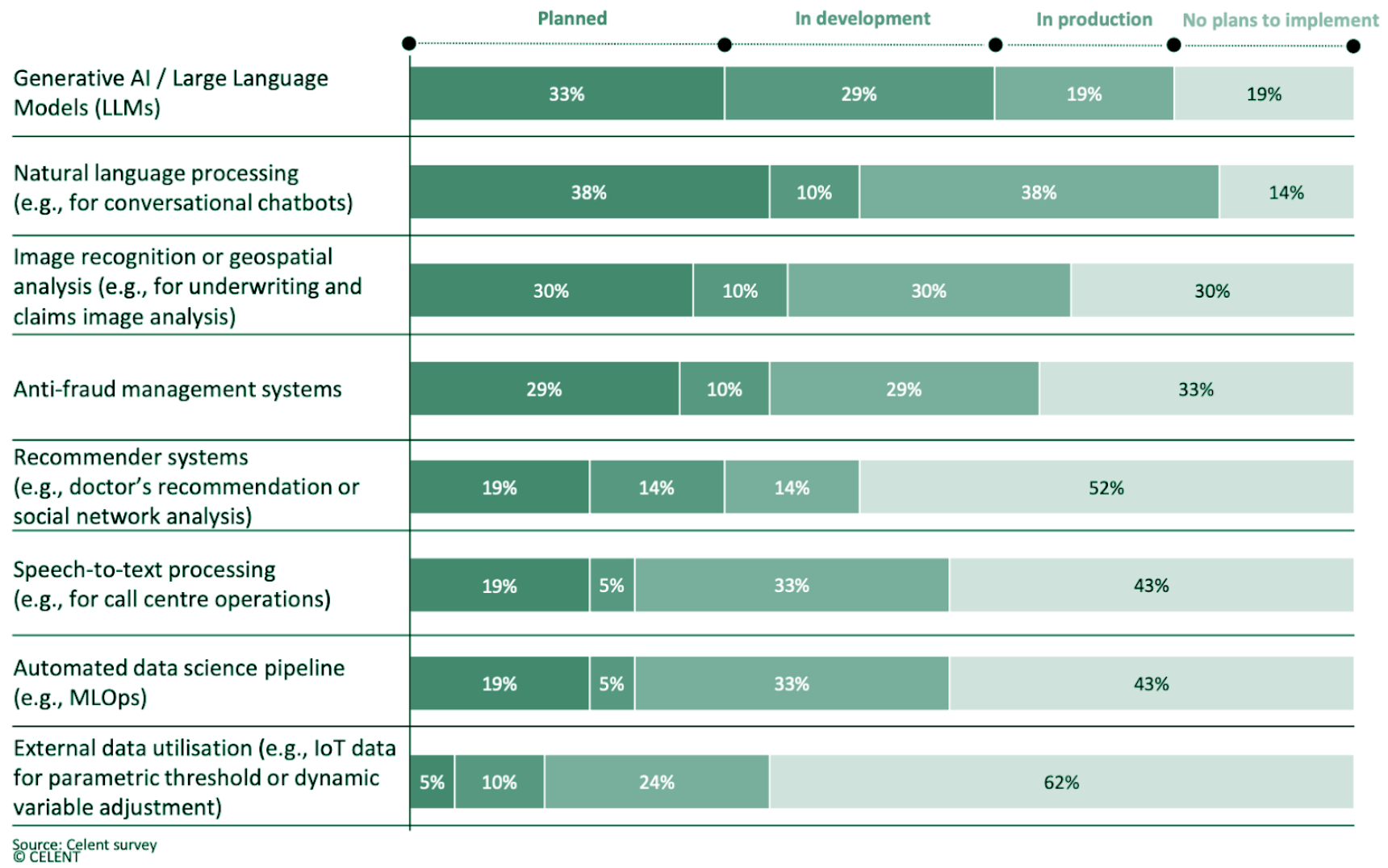
However, there’s tension between maintaining existing enterprise systems and innovating with AI. Insurance companies must balance keeping the lights on with investing in AI to meet the expectations of boards and stakeholders. The solution lies in integrating AI in a way that enhances operational efficiency without overwhelming existing systems. However, data challenges need to be addressed to achieve this, specifically around access to data. According to a Workday Global Survey, only 4% of respondents said their data is fully accessible, and 59% say their enterprise data is somewhat or completely siloed. Without a solid data foundation, insurers will struggle to achieve the benefits they are looking for from AI.
Data architectures and unstructured data
When adopting advanced technologies like AI and ML, which require data as the foundation, organizations often grapple with the challenge of integrating these innovations into legacy systems due to their inflexibility and resistance to modification. A robust data architecture is essential for future-proofing and consolidating technology investments. Insurance companies often deal with a vast amount of unstructured data, such as claim images and videos, which can be challenging to manage. By leveraging AI, specifically through vector search and large language models, companies can efficiently process and analyze this data.
MongoDB is ideal for managing unstructured data due to its flexible, JSON-like document model, which accommodates a wide variety of data types and structures without requiring a predefined schema. Additionally, MongoDB’s flexibility enables insurers to integrate seamlessly with various technologies, making it a versatile and powerful solution for unstructured data management.
For example, consider an insurance adjuster assessing damage from claim photos. Traditionally, this would require manually reviewing each image. With AI, the photos can be converted into vector embeddings and matched against a database of similar claims, drastically speeding up the process. This not only improves efficiency but also enhances the accuracy of assessments.
The converged AI and application datastore with MongoDB
Building a single view of data across various systems is a game-changer for the insurance industry. Data warehouses and data lakes have long provided single views of customer and claim data, but they often rely on historical data, which may be outdated. The next step is integrating real-time data with these views to make them more dynamic and actionable.
A versatile database platform plays a crucial role in this integration. By consolidating data into a single, easily accessible view, insurance companies can ensure that various personas, from underwriters to data scientists, can interact with the data effectively. This integration allows for more responsive and informed decision-making, which is crucial for staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
This can be achieved with a converged AI and application datastore, as shown in Figure 2 below. This is where operational data, analytics insights, and unstructured data become operationally ready for the applications that leverage AI.
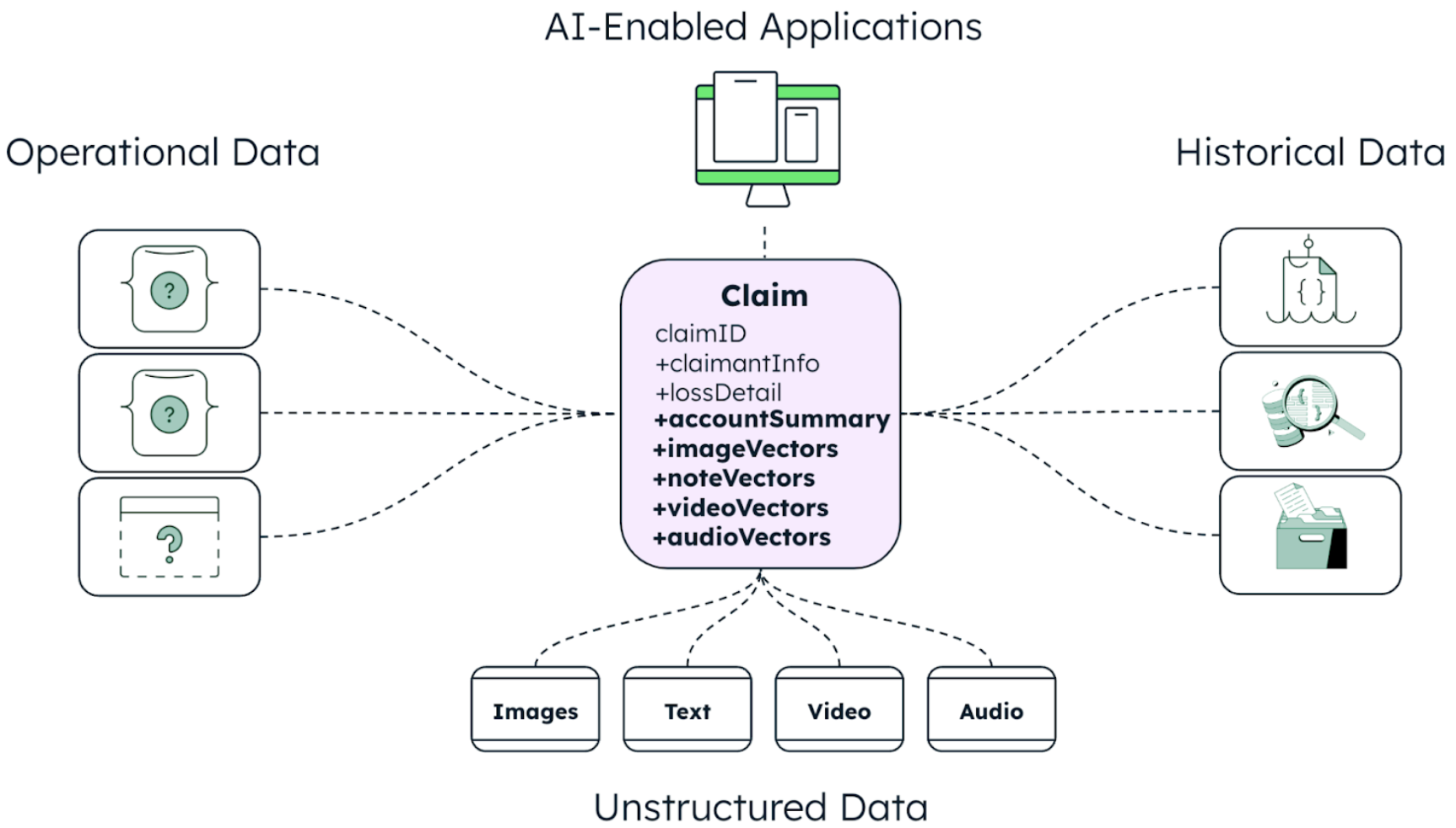
The convergence of AI, data, and application datastores is reshaping the insurance industry. By making smart technology investments, leveraging AI to manage unstructured data, and building robust data architectures, insurance companies can future-proof their operations and embrace innovation. A versatile and flexible data platform provides the foundation for these advancements, enabling companies to make their data more accessible, actionable, and valuable.
The MongoDB Atlas developer data platform puts powerful AI and analytics capabilities directly in the hands of developers and offers the capabilities to enrich applications by consolidating, ingesting, and acting on any data type instantly. Because MongoDB serves as the operational data store (ODS)—with its flexible document model—insurers can efficiently handle large volumes of data in real-time. By integrating MongoDB with AI/ML platforms, insurers can develop models trained on the most accurate and up-to-date data, thereby addressing the critical need for adaptability and agility in the face of evolving technologies.
With built-in security controls across all data, whether managed in a customer environment or through MongoDB Atlas, a fully managed cloud service, MongoDB ensures robust security with features such as authentication (single sign-on and multi-factor authentication), role-based access controls, and comprehensive data encryption. These security measures act as a safeguard for sensitive data, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access from external parties and providing organizations with the confidence to embrace AI and ML technologies.
If you would like to learn more about the convergence of AI and application datastores, visit the following resources:
-
Video: The Converged AI and Application Datastore: How API’s, AI & Data are Reshaping Insurance
-
The MongoDB Solutions Library is curated with tailored solutions to help developers kick-start their projects