Welcome to the Ansible Lightspeed with IBM Watson Code Assistant Technical Preview
At Red Hat Summit and AnsibleFest 2023, we announced Ansible Lightspeed with IBM Watson Code Assistant, a new generative AI service for Ansible automation.
Today, we are thrilled to announce the Ansible Lightspeed technical preview launch.
In this blog, we’ll walk through the steps to access the Ansible
Lightspeed with IBM Watson Code Assistant technical preview service and
get it up and running in your Visual Studio Code environment. Then we’ll
share more about what you can expect from the experience and how to
generate your first Ansible tasks with generative AI.
This is exciting stuff, so let’s dive right in.
Technical Preview: Empowering Ansible Users with AI
Ansible Lightspeed with IBM Watson Code Assistant is a purpose-built
generative AI tool that aims to streamline the creation of Ansible
content. This capability is natively integrated into your VS Code editor
via the Ansible VS Code extension.
The AI capabilities are powered by Watson Code Assistant, a foundation
model trained on Ansible Galaxy, GitHub, and other open sources of
data.
The technical preview is open and available, free of charge, to all
Ansible users. As more users engage with Ansible Lightspeed, the model
recommendations will continuously improve, thanks to the valuable input
and engagement from the community.
Getting Connected: Installation and Configuration
You’ll need Visual Studio Code and Ansible installed on
your workstation and a GitHub account to access the Ansible Lightspeed
service. Let’s get started!
- Install the Ansible VS Code extension from the Visual Studio Code Marketplace by
searching for “ansible” and selecting the extension published by Red Hat. - Enable the Ansible Lightspeed service within the extension by accessing the “Extension Settings” via the gear icon.
- In the settings, enable both “Ansible Lightspeed enabled” and “Enable Ansible Lightspeed with Watson Code Assistant inline suggestions” checkboxes.
Note: You can enable Ansible Lightspeed in the “[User]” or “[Workspace]”
settings, based on your preference. More information on VS Code User and
Workspace settings can be found in their
documentation.
Installing the Ansible Visual Studio Code extension.
- Click on the Ansible “A” in the VS Code activity bar on the
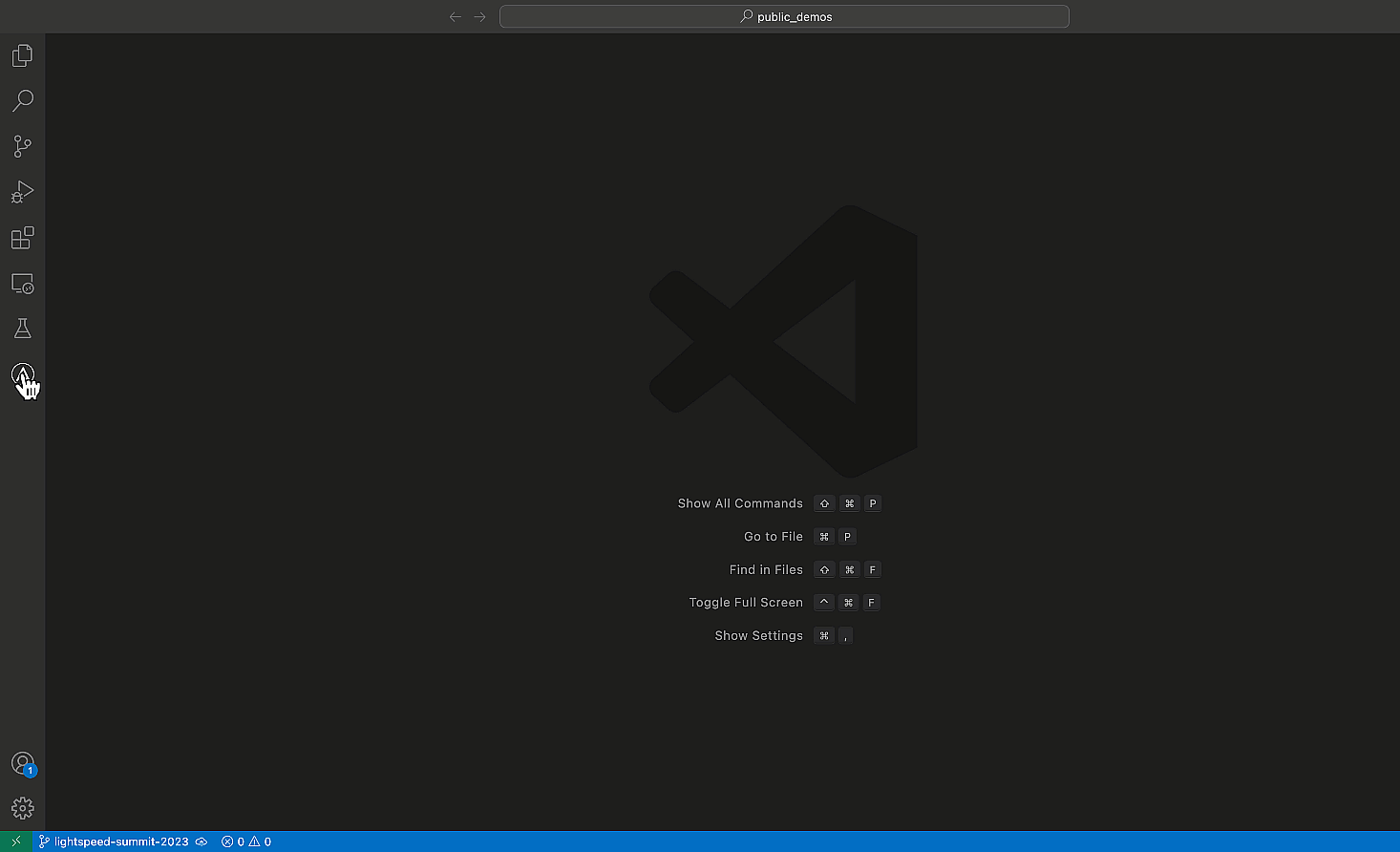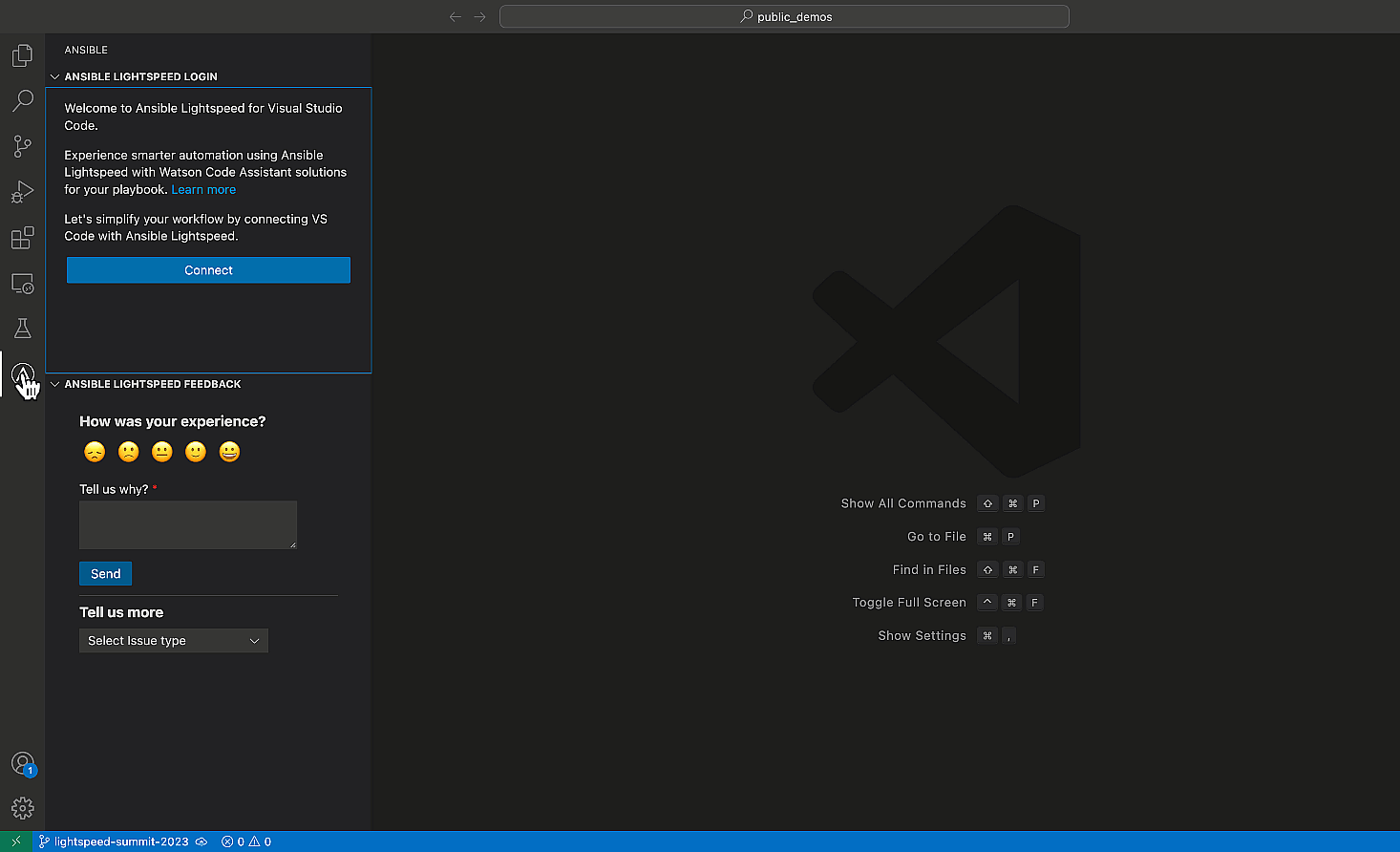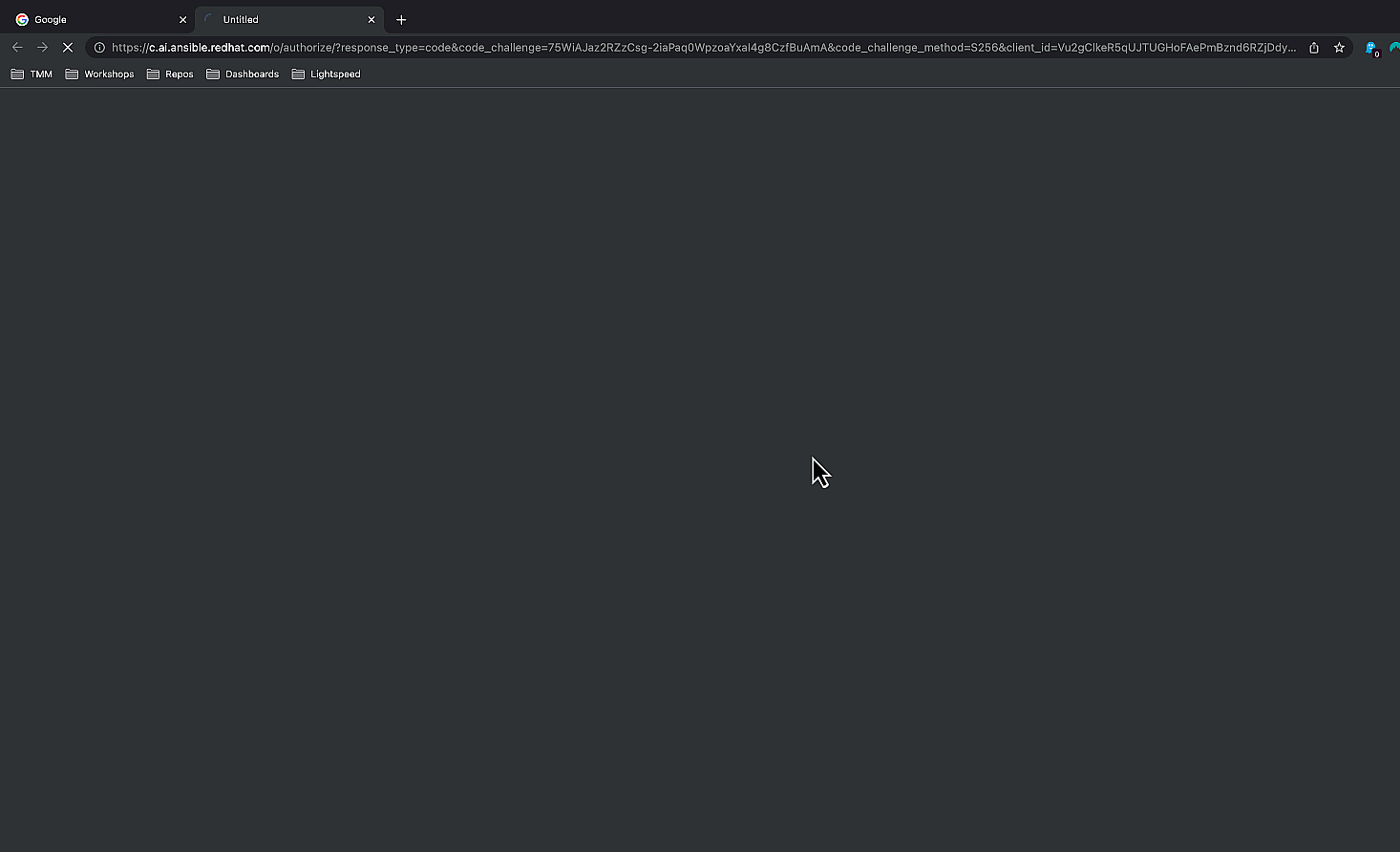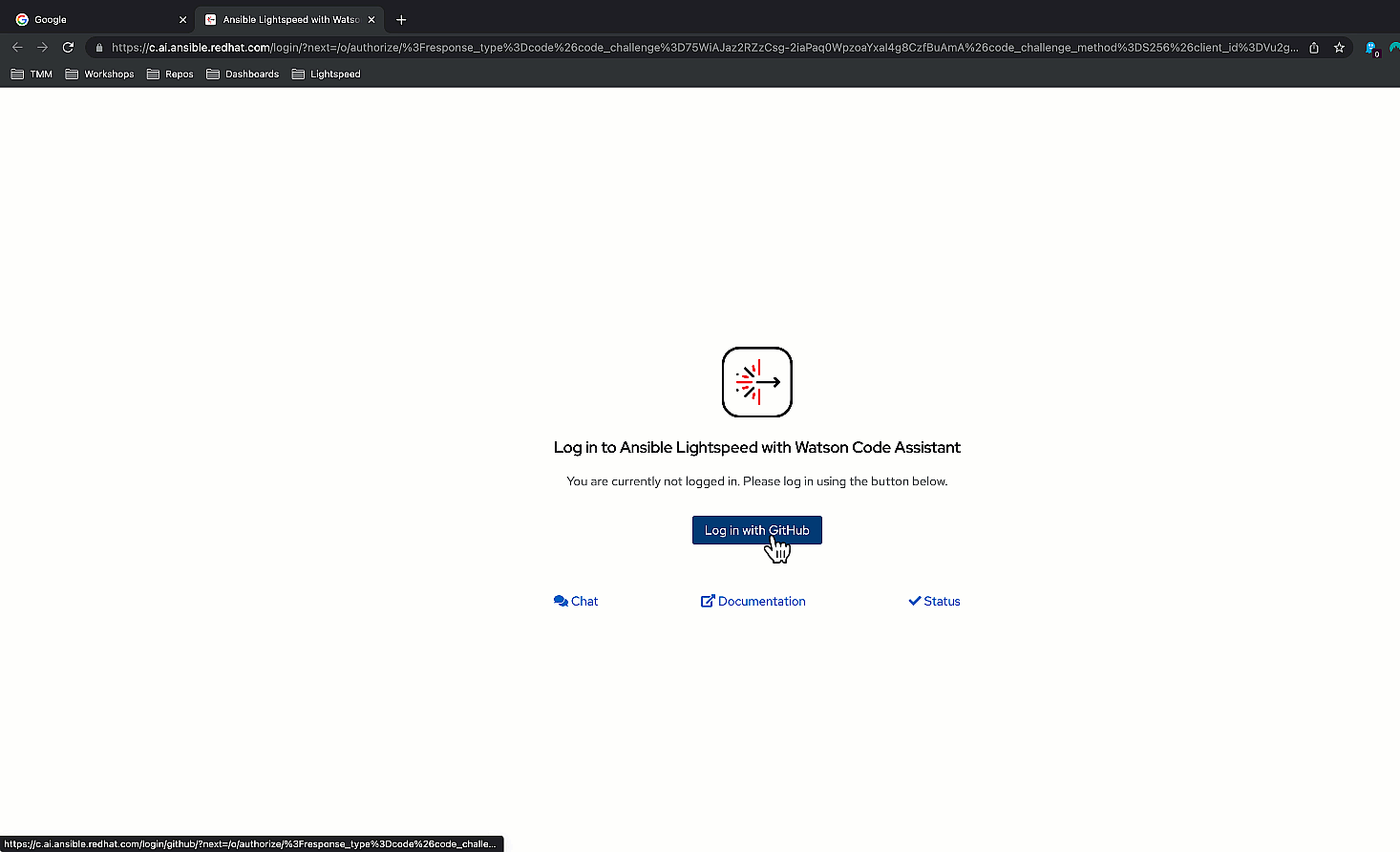
left-hand side of your editor to open the extension. - Click “Connect” and follow the prompts to log into GitHub using
your credentials.
Log in using your GitHub credentials.
- Read the Ansible Lightspeed technical preview terms and conditions and click “Agree“.
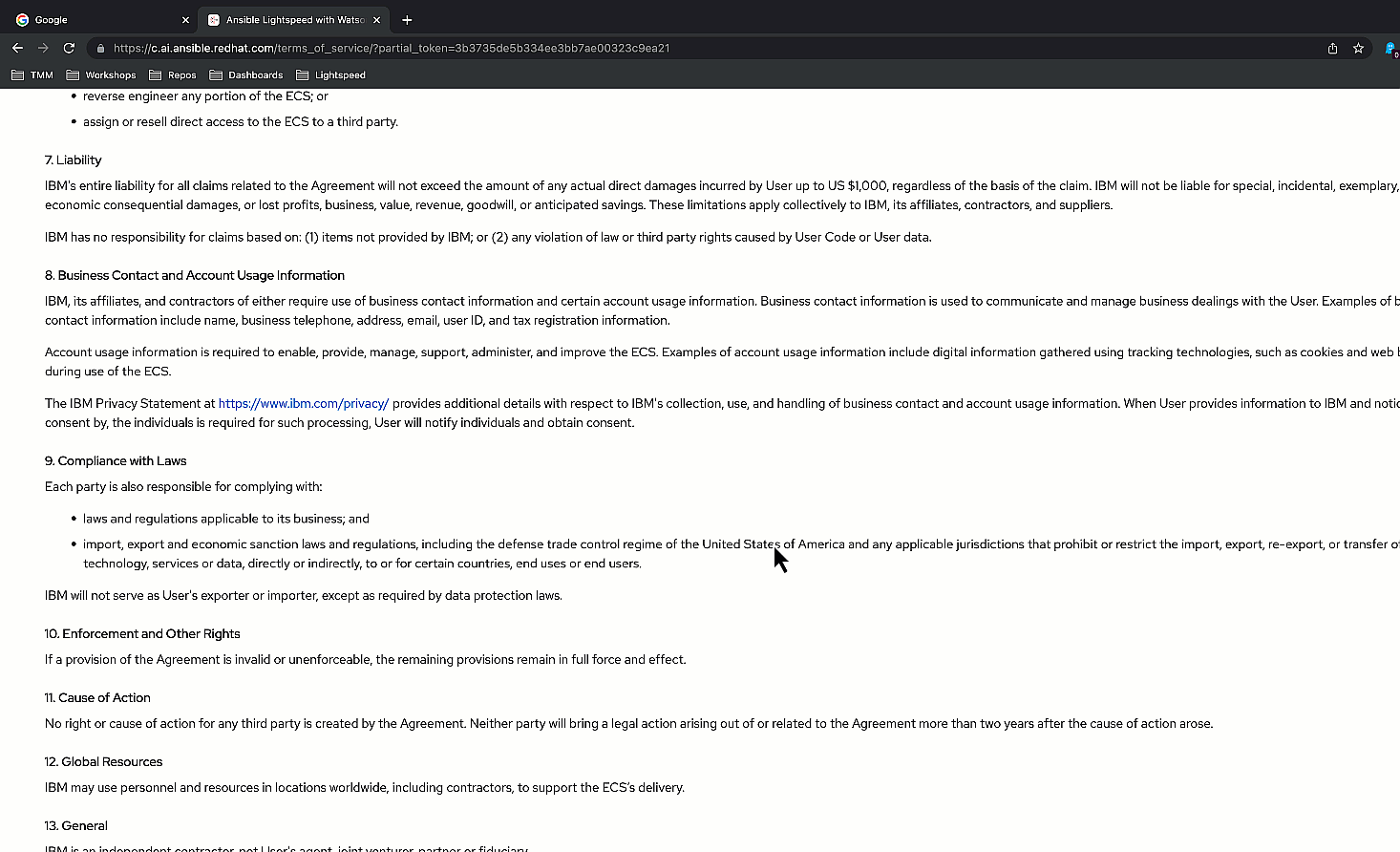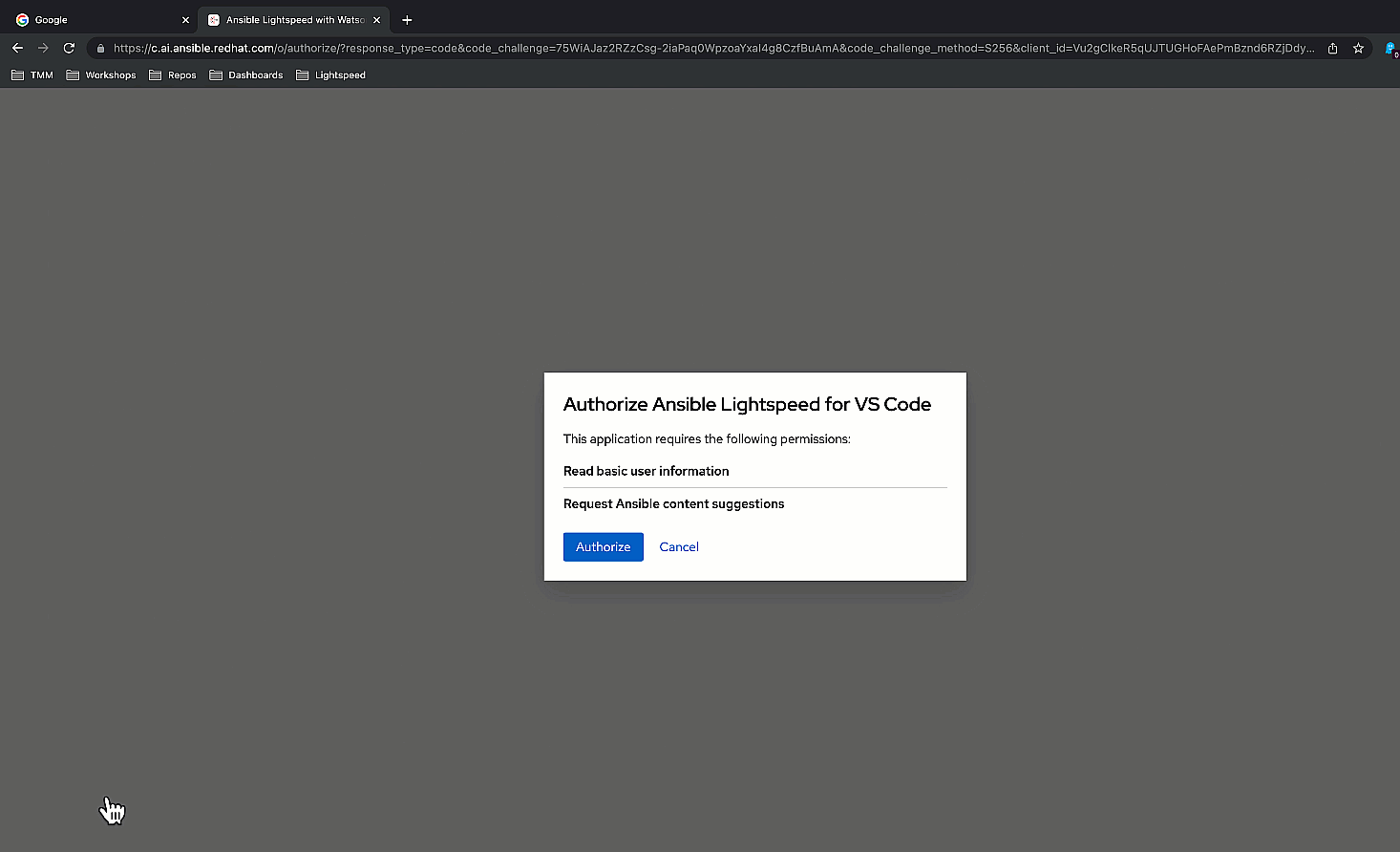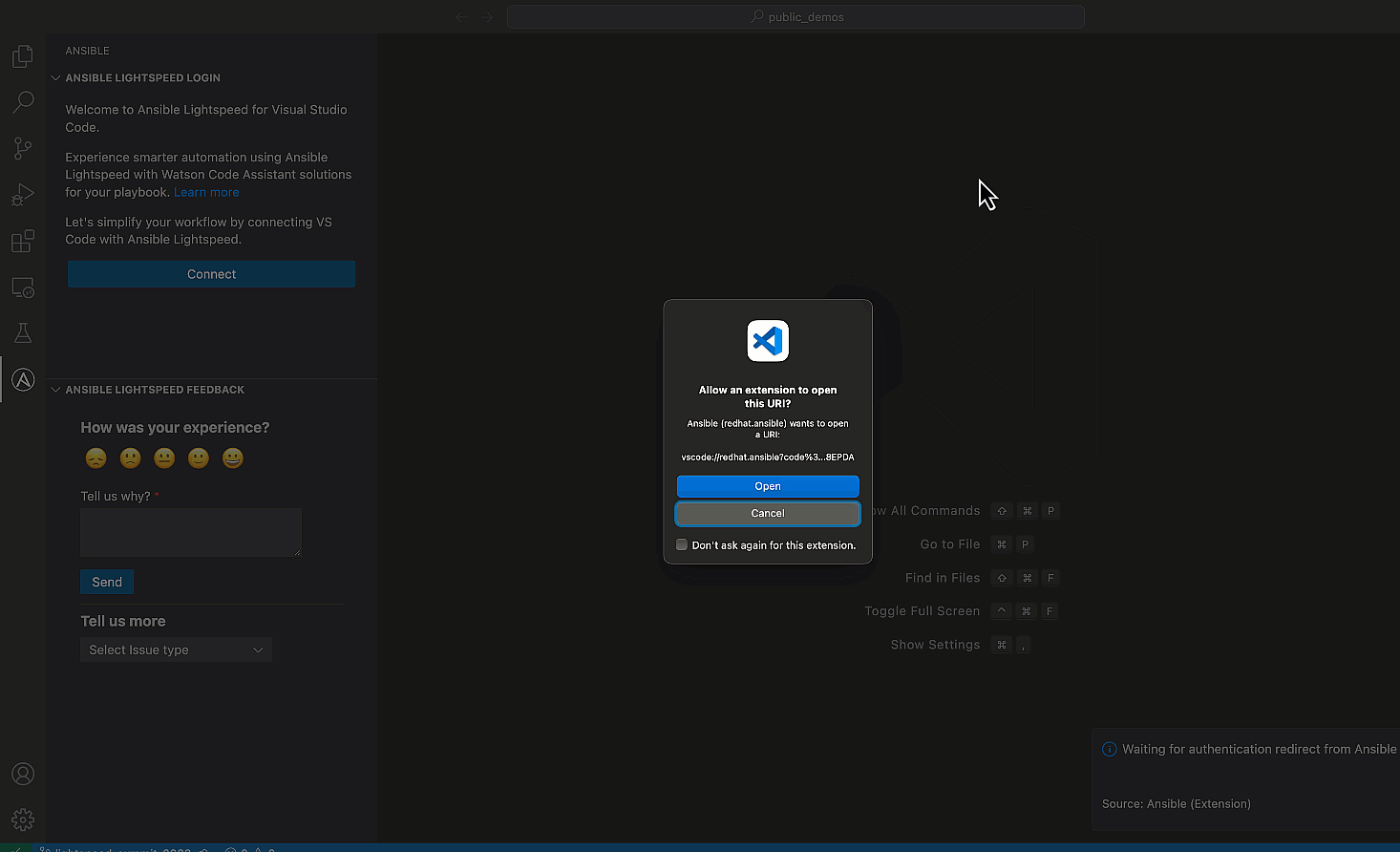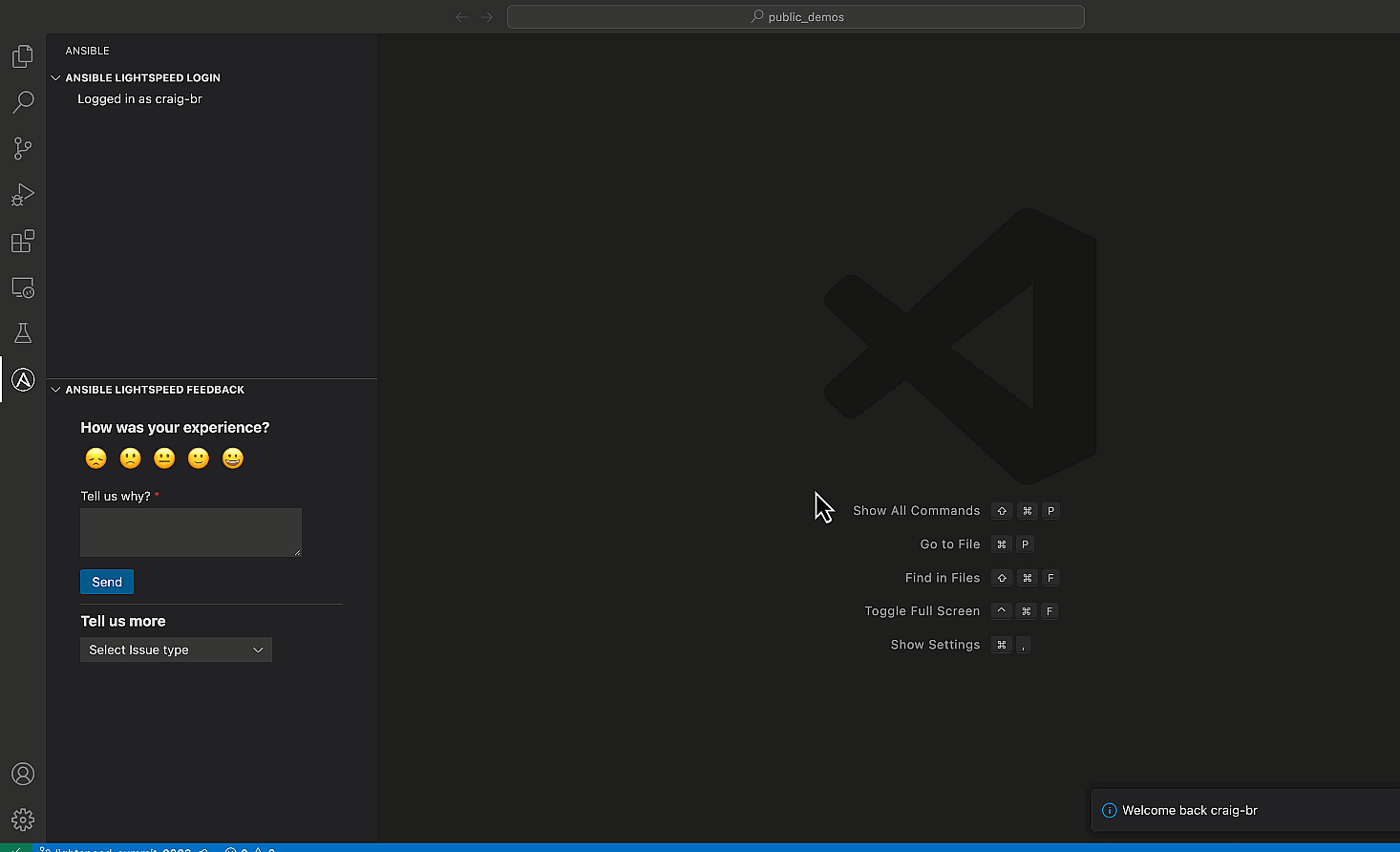
- Next, authorize Ansible Lightspeed for VS Code by clicking “Authorize“.
- Follow the browser prompts to redirect you back to VS Code, and, finally, click “Open” in the VS Code confirmation dialog box.
Authorize Ansible Lightspeed.
Congratulations! You’ve successfully configured Ansible Lightspeed in VS
Code.
You can confirm that Ansible Lightspeed is enabled by checking the VS
Code status bar at the bottom of the editor window.
Please ensure a Python environment is selected and your Ansible YAML
files are associated with the Ansible language. More information on VS
Code languages can be found in their
documentation.
Ansible Lightspeed status.

A Quick Tour of Ansible Lightspeed: Generating Your First Task
Now that you are connected to Ansible Lightspeed, it’s time to
experience its AI-enhanced content creation experience.
Let’s use an
example
Playbook
to walk through asking Ansible Lightspeed for AI-generated task suggestions and also highlight some of what you can
expect in the technical preview release. The example Playbook installs
Cockpit
on a Red Hat Enterprise Linux system.
Note: As more users engage with Ansible Lightspeed, the breadth, depth, and quality of the recommendations generated by the model will improve. Therefore, the Ansible task suggestions in the examples below may differ from your results.
How do I generate an Ansible Lightspeed suggestion?
Let’s use our first Playbook task in the
deploy_monitoring.yml
example Playbook to demonstrate asking Ansible Lightspeed for an AI suggestion.
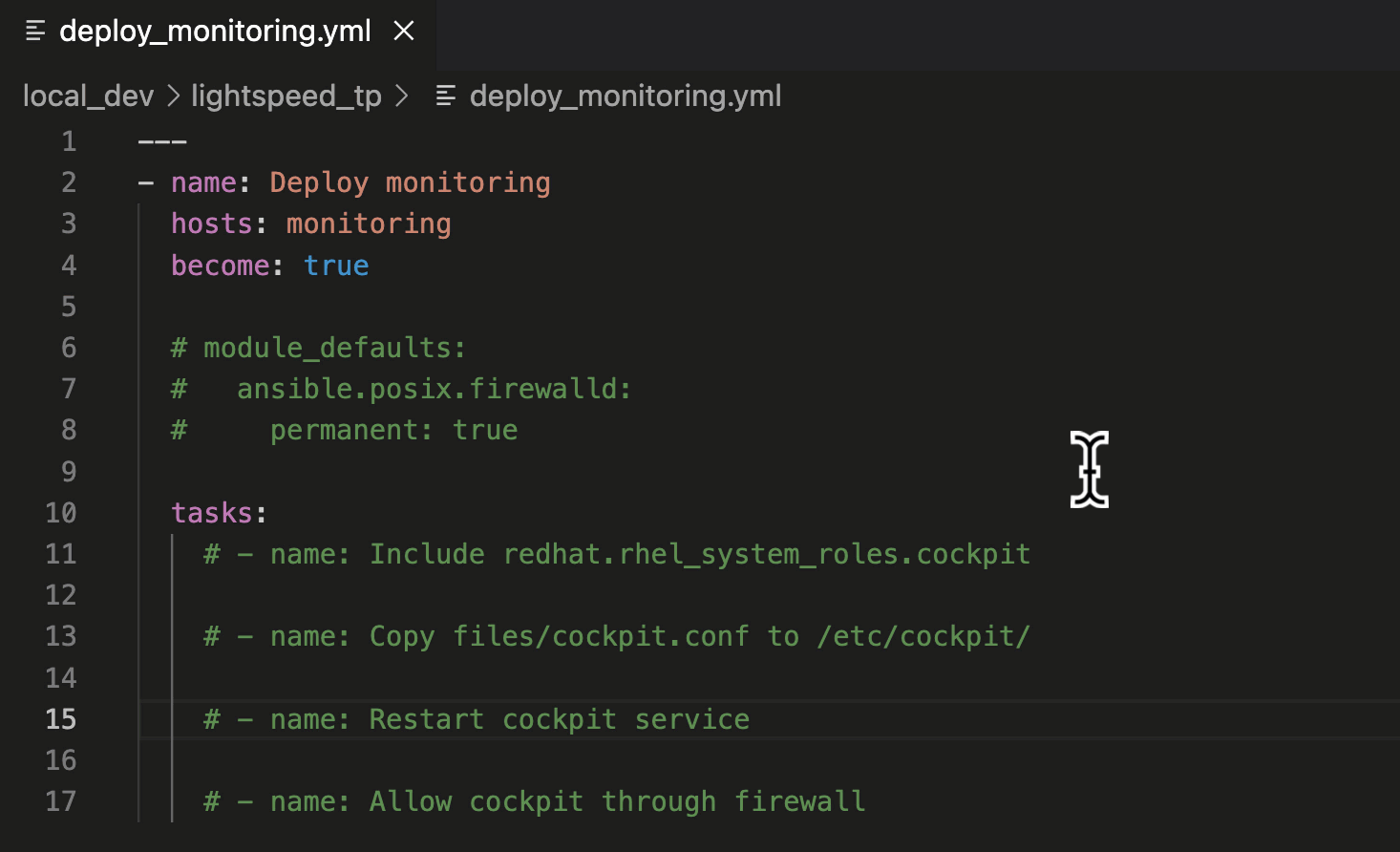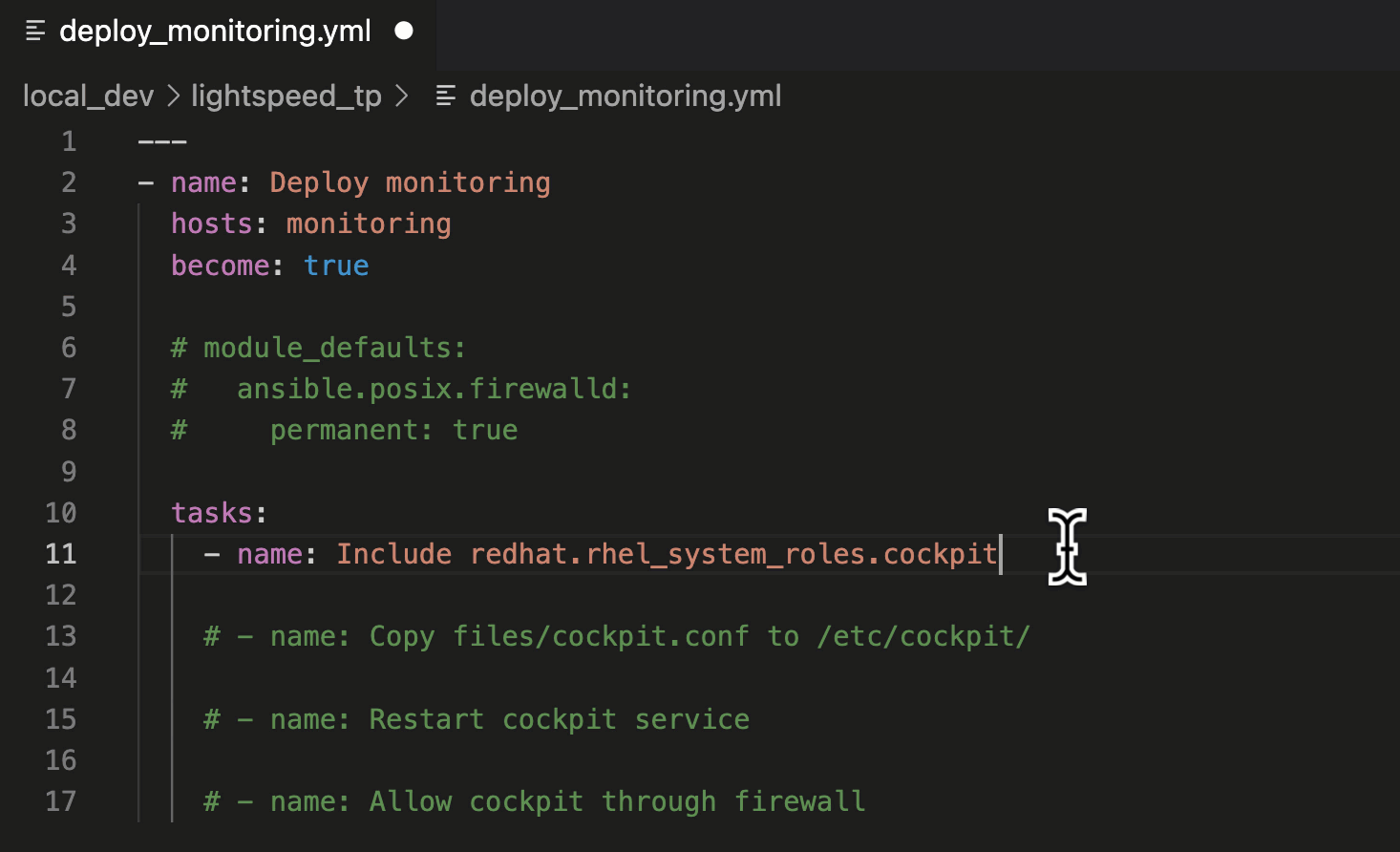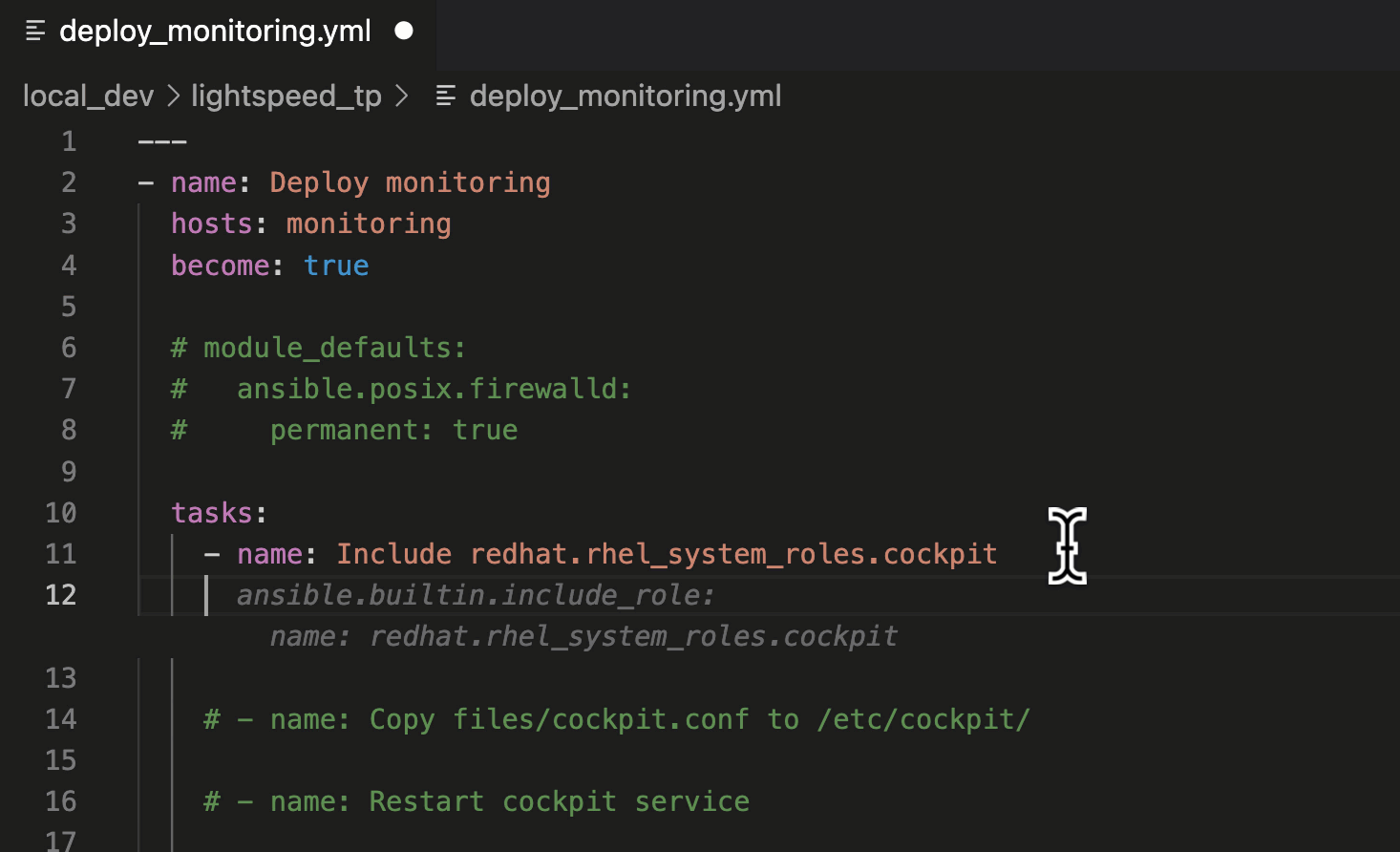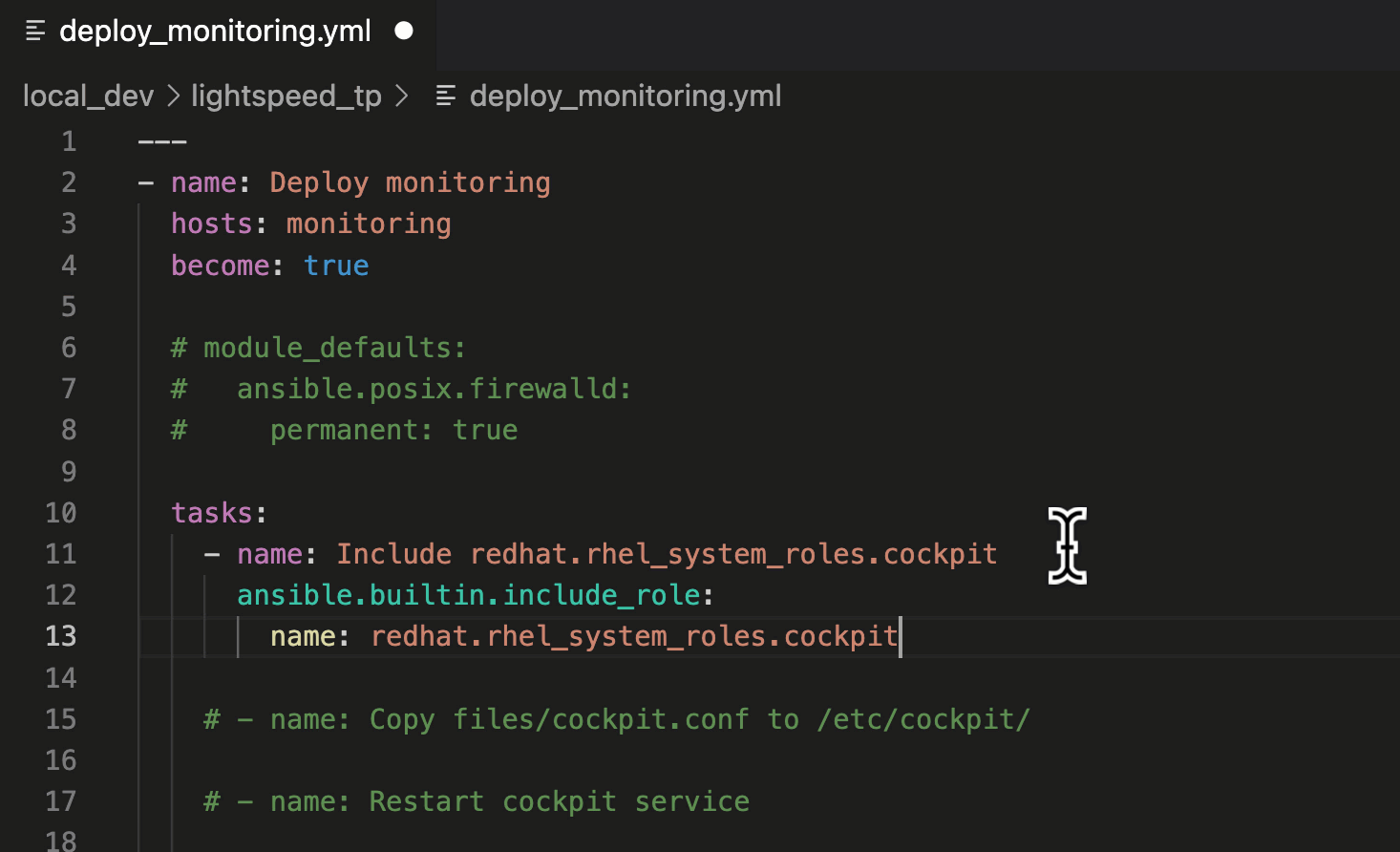
- Move your cursor to the end of the “– name: Include redhat.rhel_system_roles.cockpit” task description.
- Press “ENTER” to generate a suggestion.
- Press “TAB” to accept the suggestion.
Generating an Ansible task.
In this suggestion, we asked Ansible Lightspeed to include the
“cockpit” Role, part of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux System Roles Certified Content Collection. The suggestion used the Fully Qualified Collection Name (FQCN):
ansible.builtin.include_role.
Using FQCNs is a recommended best practice and an example of the many unique post-processing capabilities we’ve baked into the Ansible Lightspeed service.
Let’s move on to the next task.
Ansible best practices. We’ve got you covered.
Ansible Lightspeed best practices example.
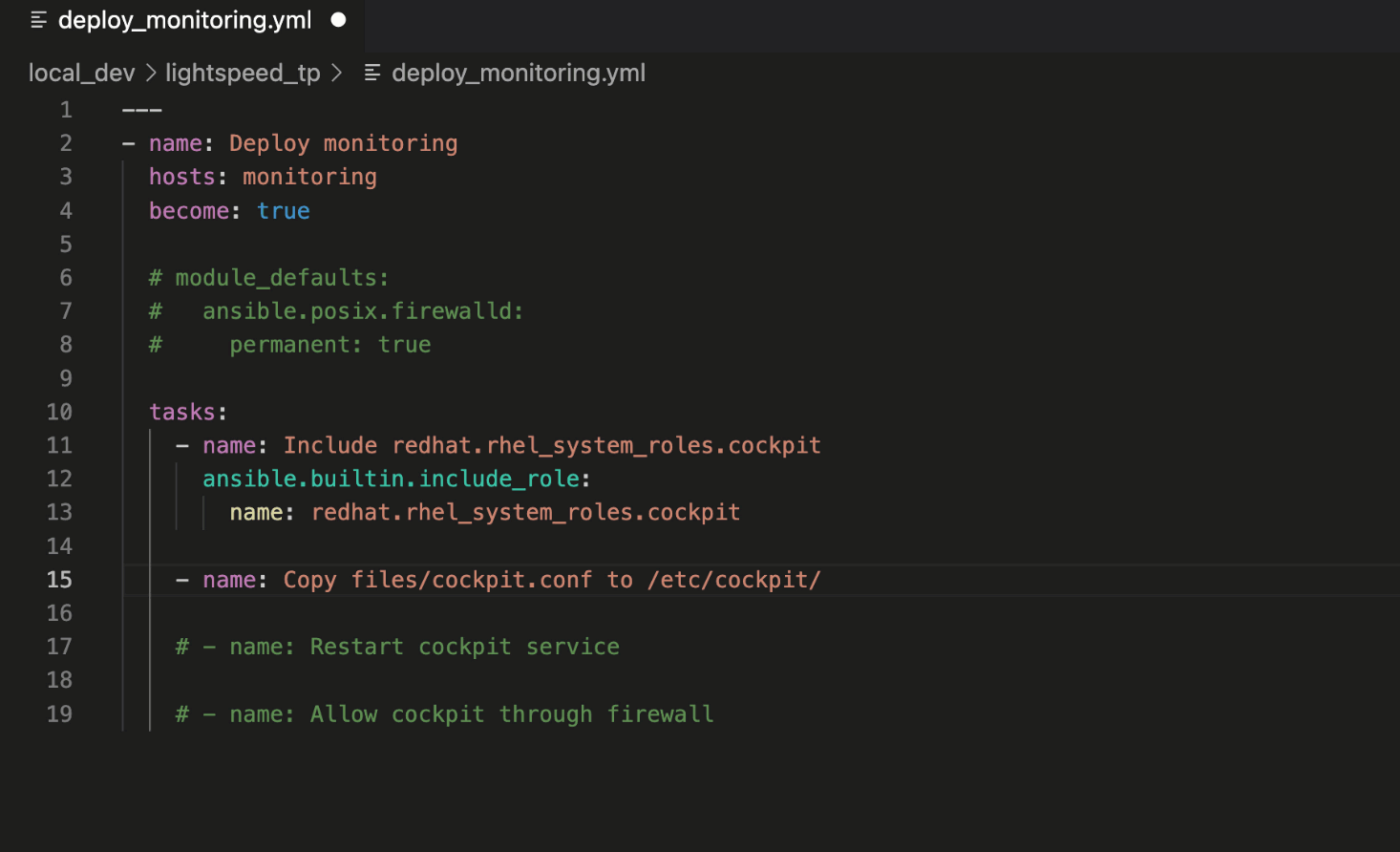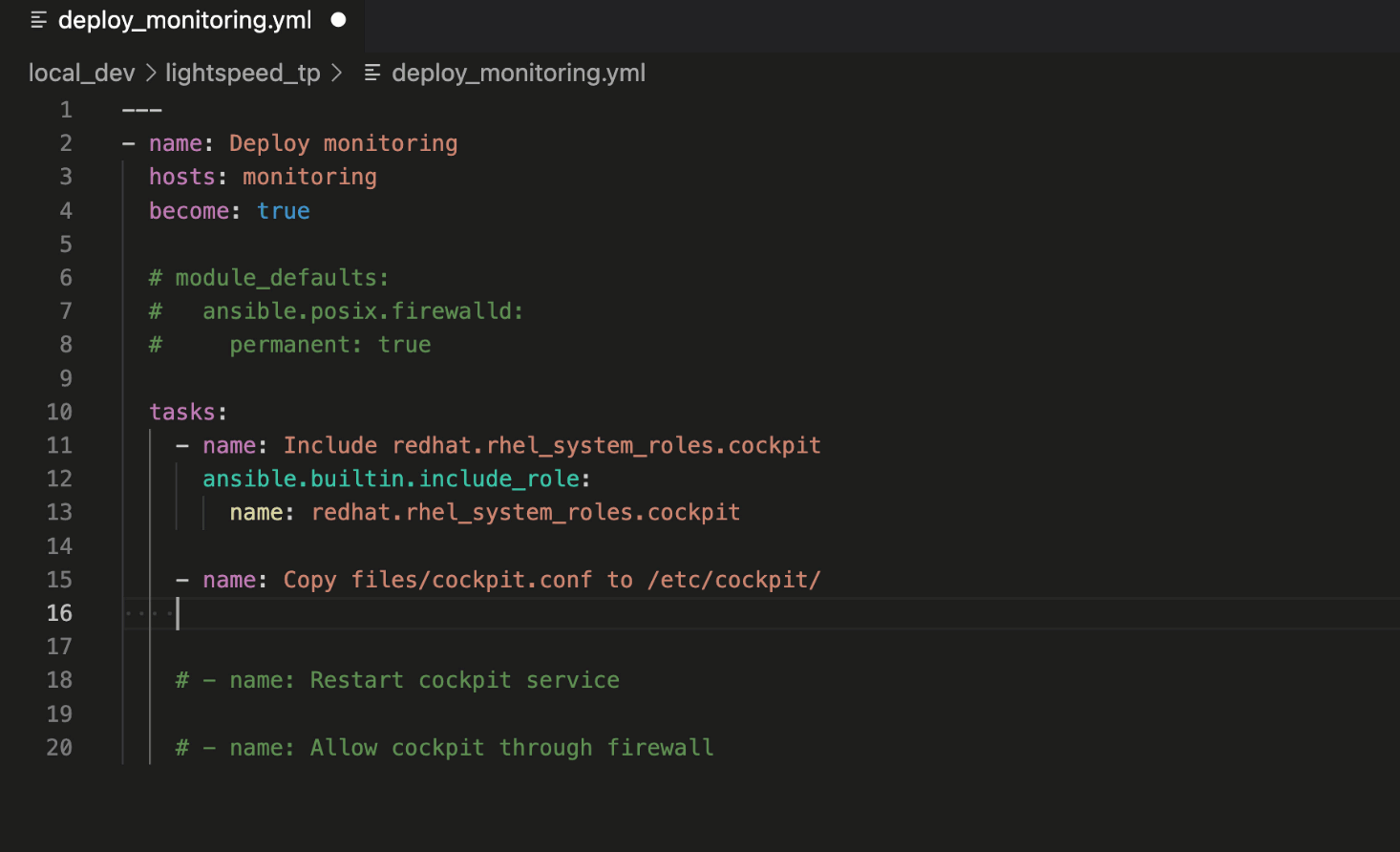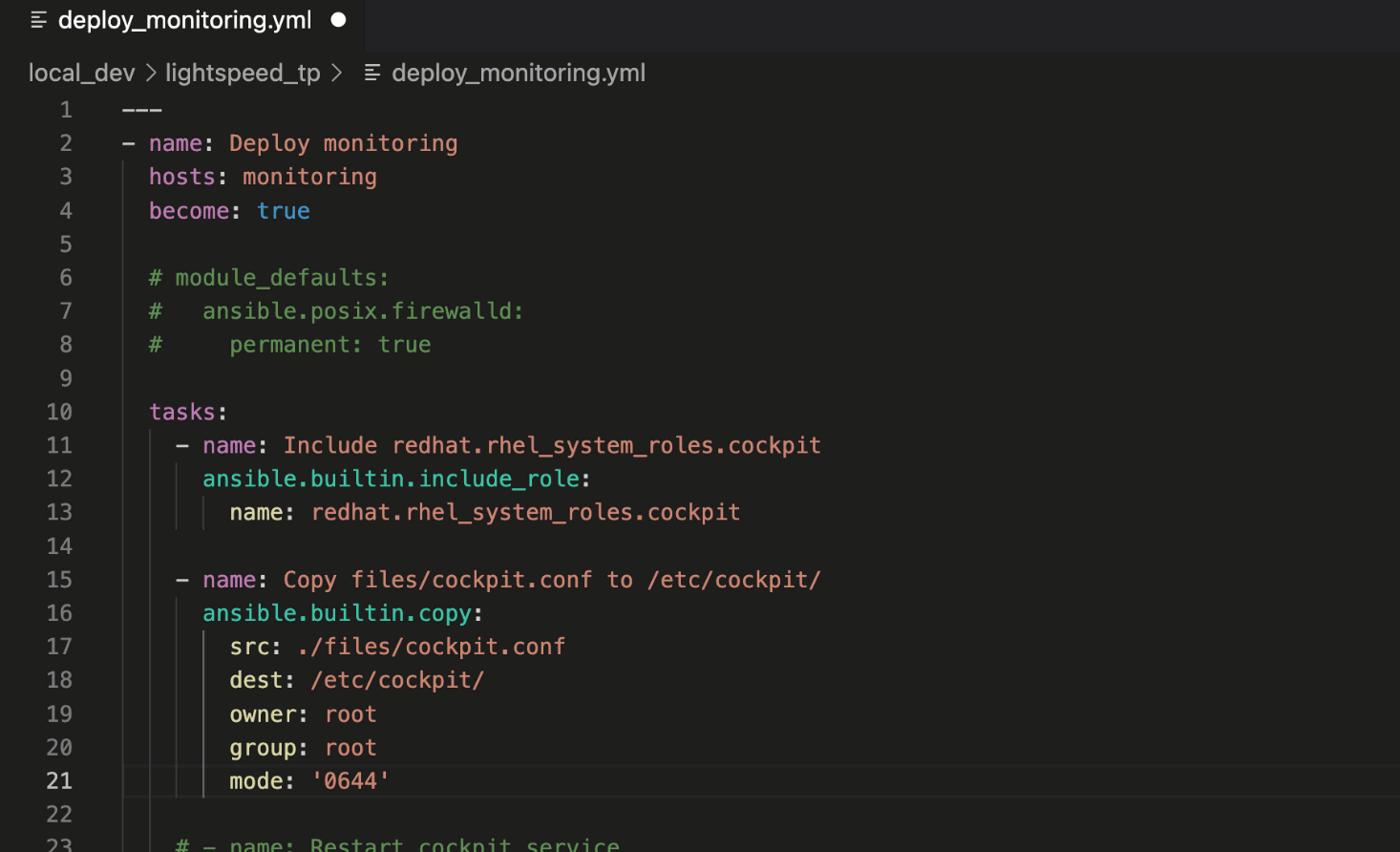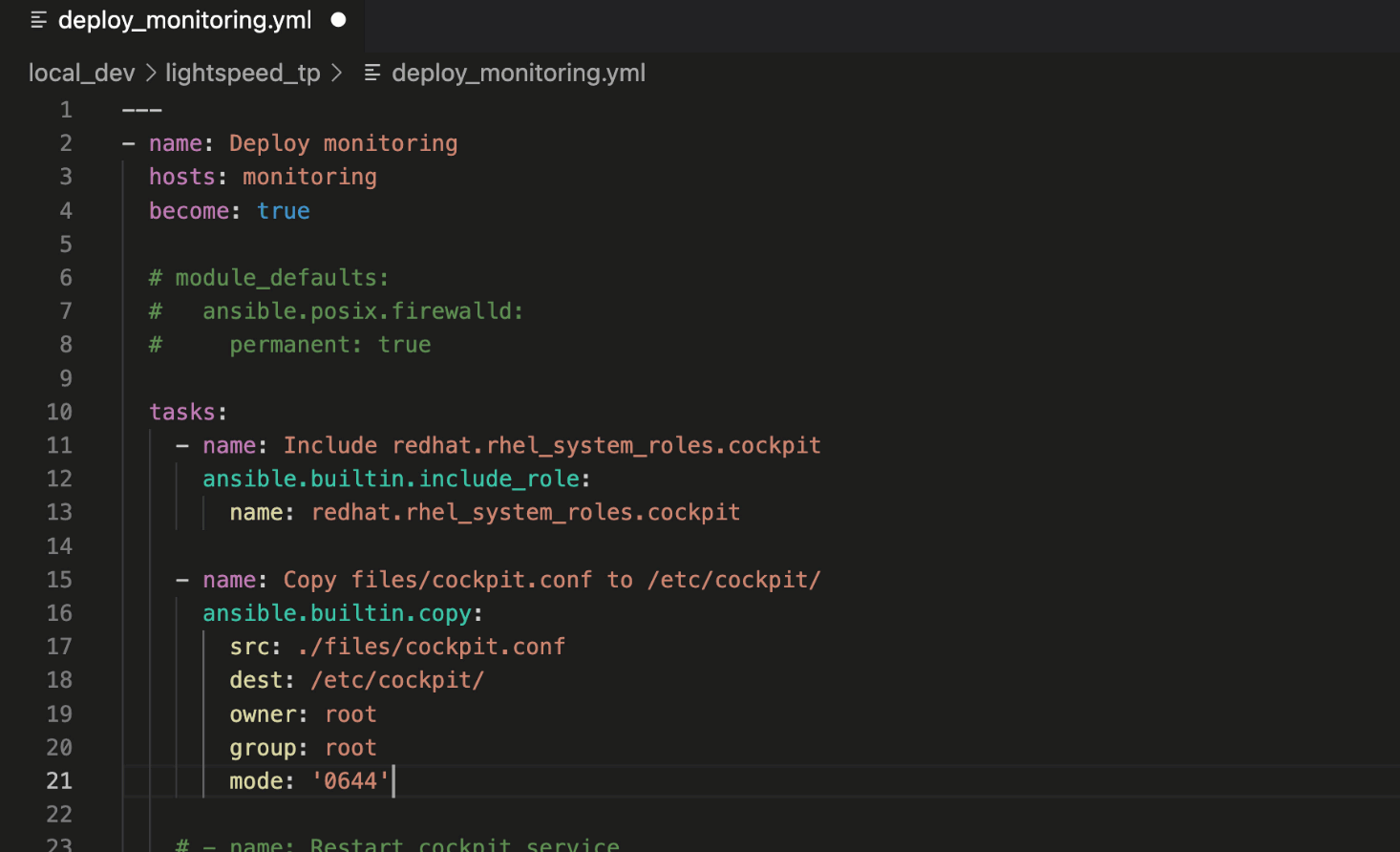
This Playbook task copies
cockpit.conf to the target host. Note that the recommendation included the “mode:” module argument and set the Linux file permissions to 0*644*.
Ansible Lightspeed provided a robust example of setting file permissions
for the ansible.builtin.copy module, another recommended best practice.
We’ll continue to expand on these natively integrated best practices as the service matures.
Finalizing the Playbook
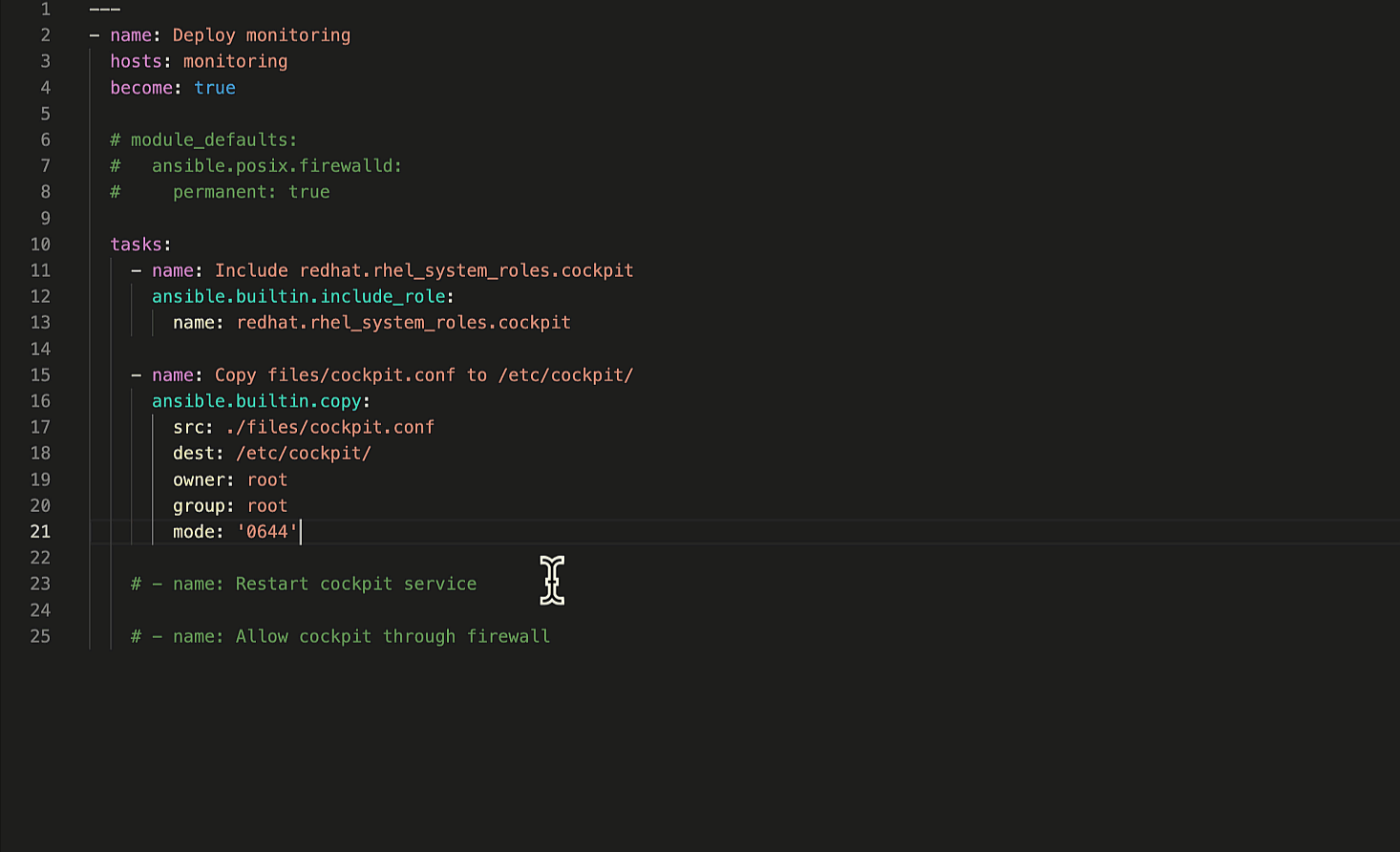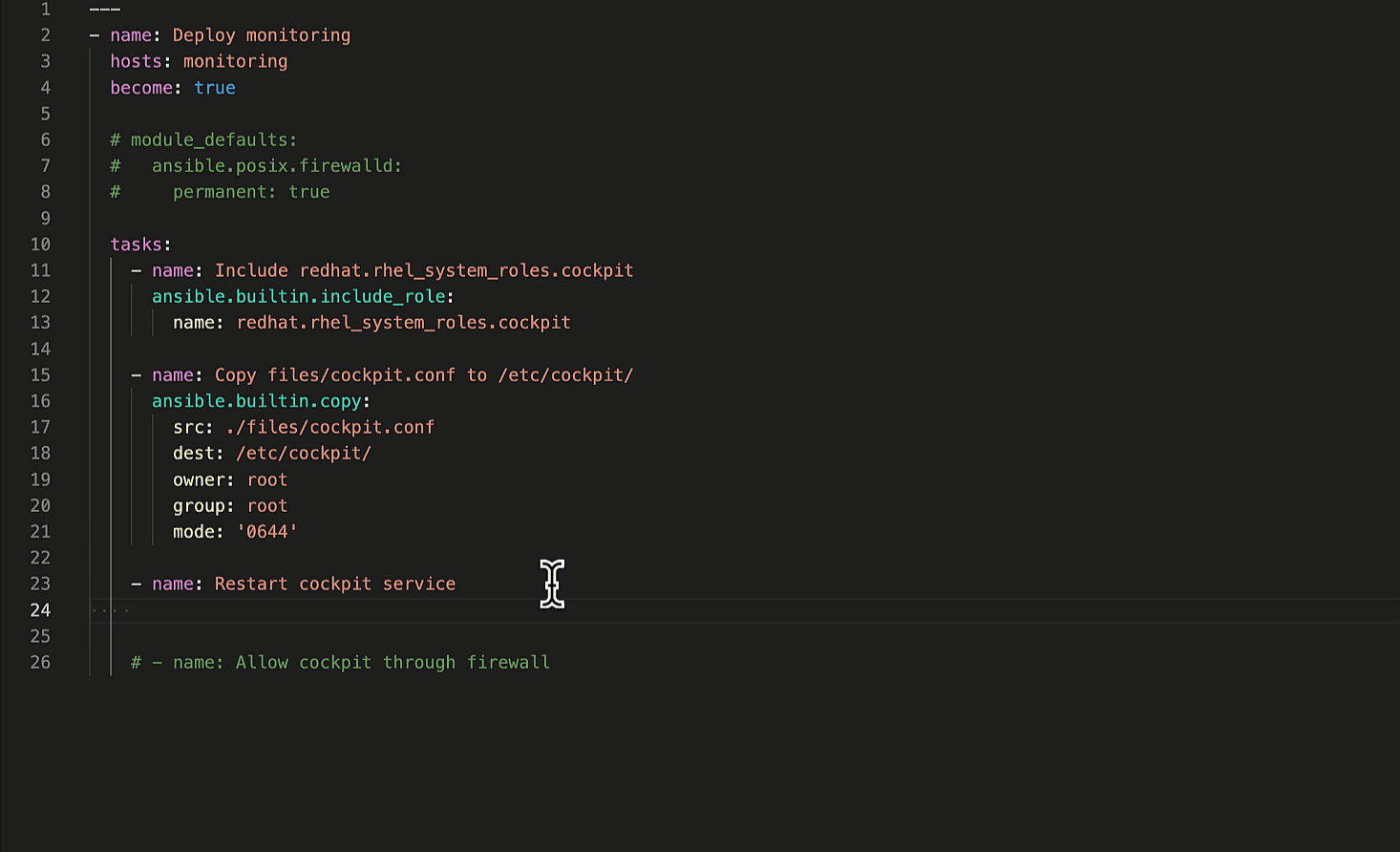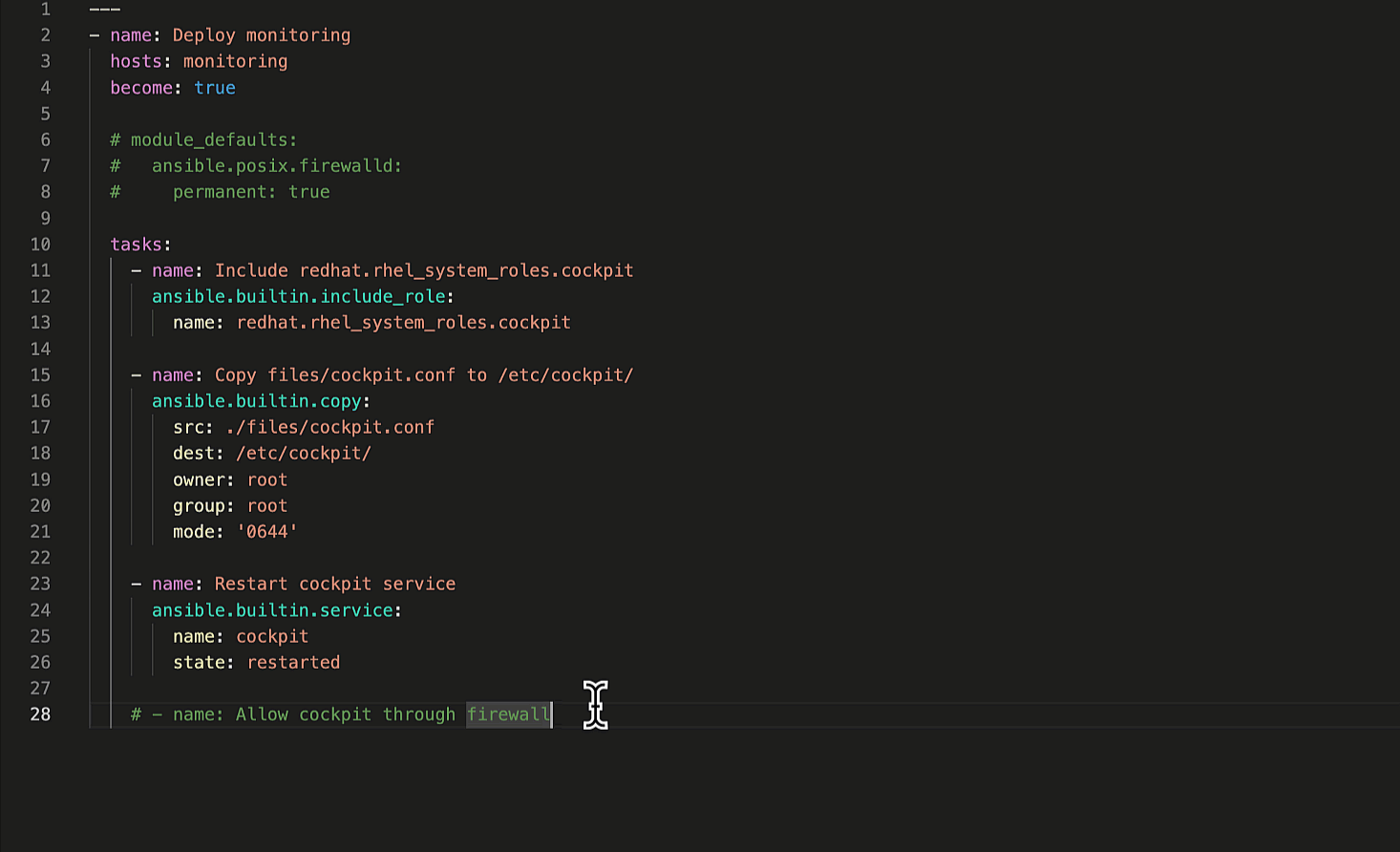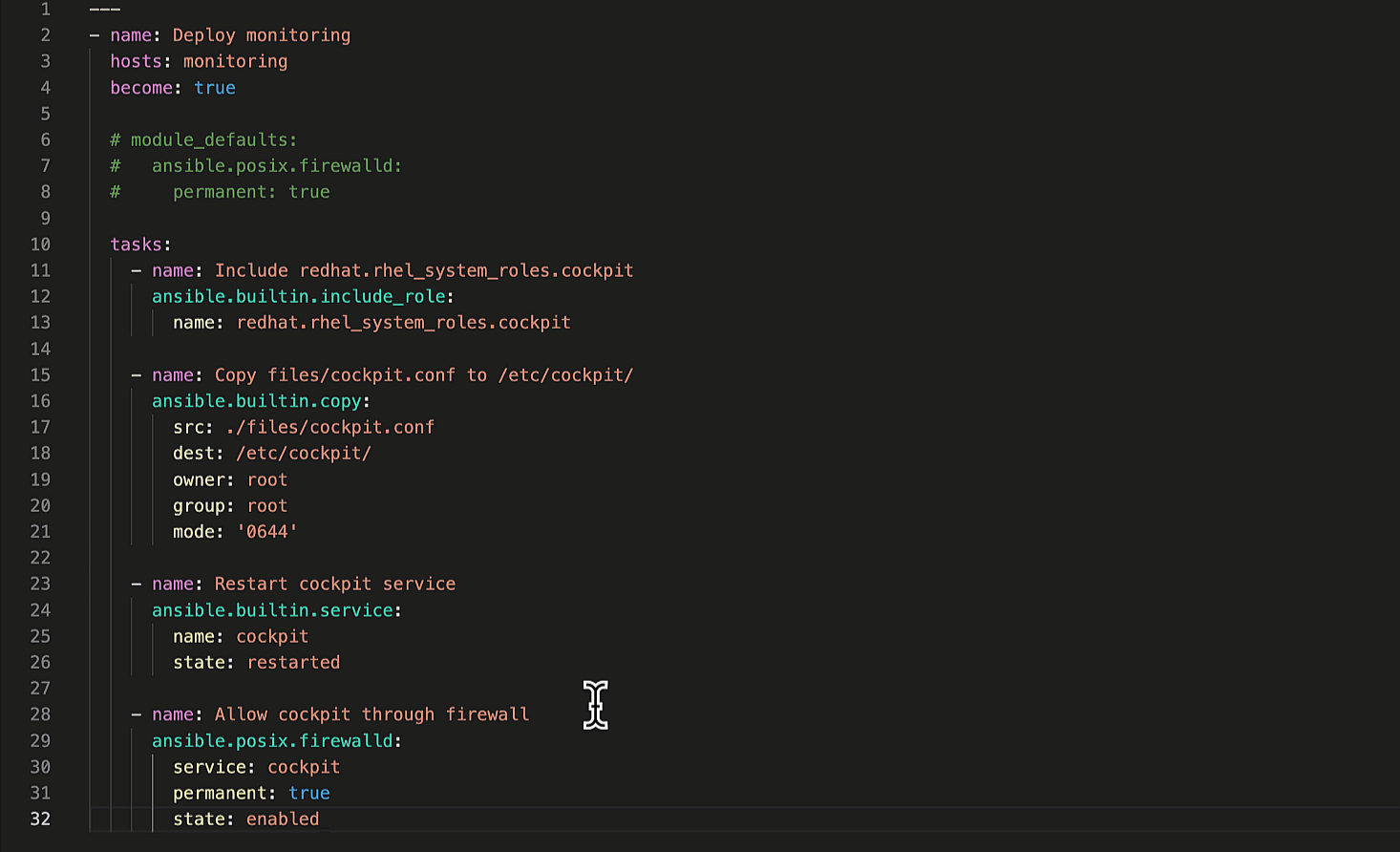
Let’s ask Ansible Lightspeed to generate suggestions for the remaining
two Playbook tasks. The first task restarts the Cockpit service to apply our custom
cockpit.conf
configuration file and the second task permits Cockpit service traffic through the firewall.
Generate remaining Ansible tasks.
Ansible Lightspeed with Watson Code Assistant and context
Generating contextually aware, accurate Ansible content suggestions
saves you time and helps you create efficiently. One of Ansible
Lightspeed’s superpowers is context.
Ansible Lightspeed uses the Ansible task description and YAML file
content to generate suggestions suited to what you’re automating. Let’s
use an example to illustrate this.
Imagine we want to set module defaults for the
ansible.posix.firewalld
module in the last Ansible task. Specifically, always
making the firewall rule changes permanent. We can accomplish this by using the
module_defaults Playbook keyword, illustrated below.
module_defaults: ansible.posix.firewalld: permanent: true
Ansible Playbook module_defaults section
The module defaults section tells Ansible to always add “permanent: true”
to every “ansible.posix.firewall” task in the Playbook. Let’s
ask Ansible Lightspeed for an updated suggestion with the module
defaults.
Ansible Lightspeed context.
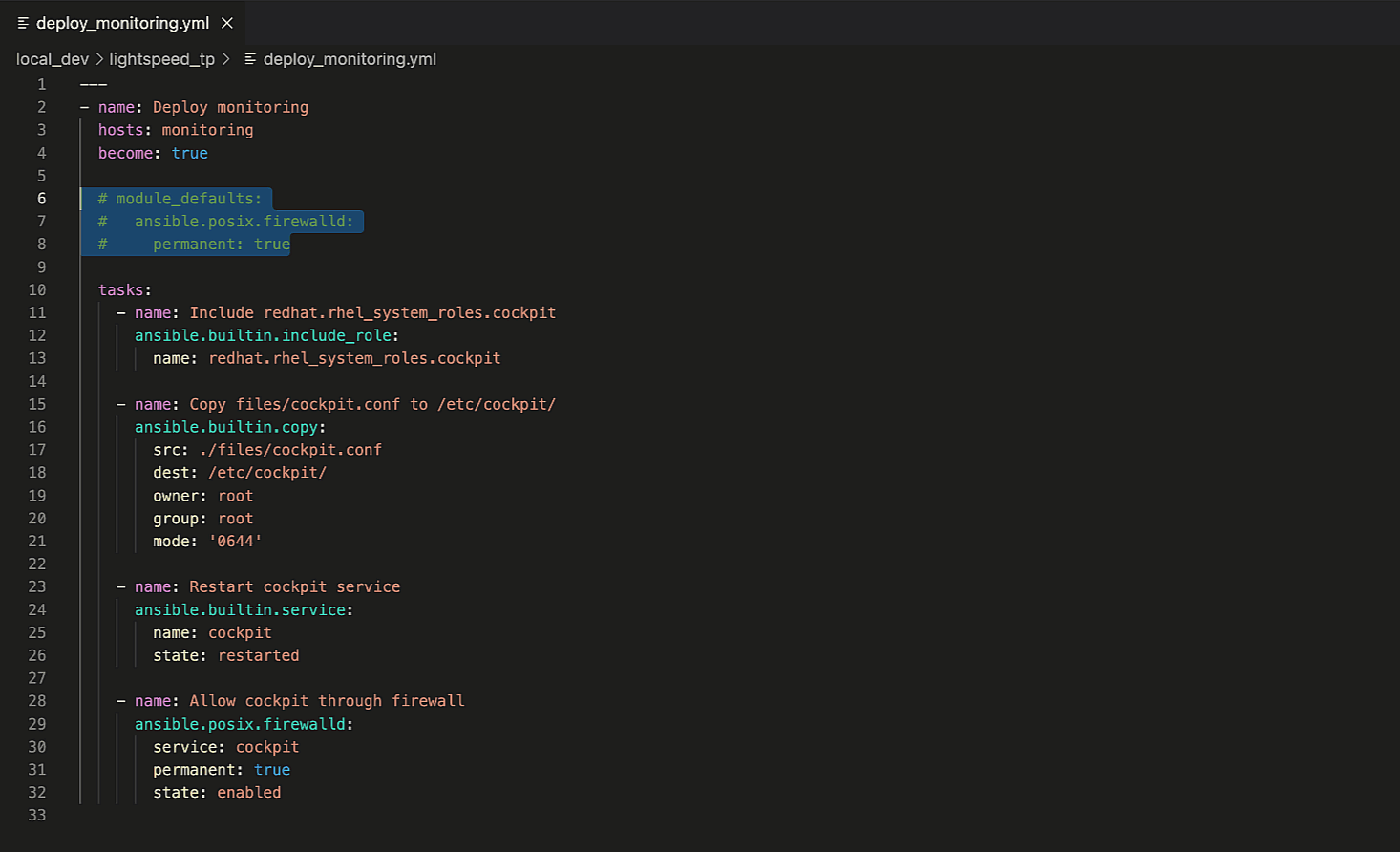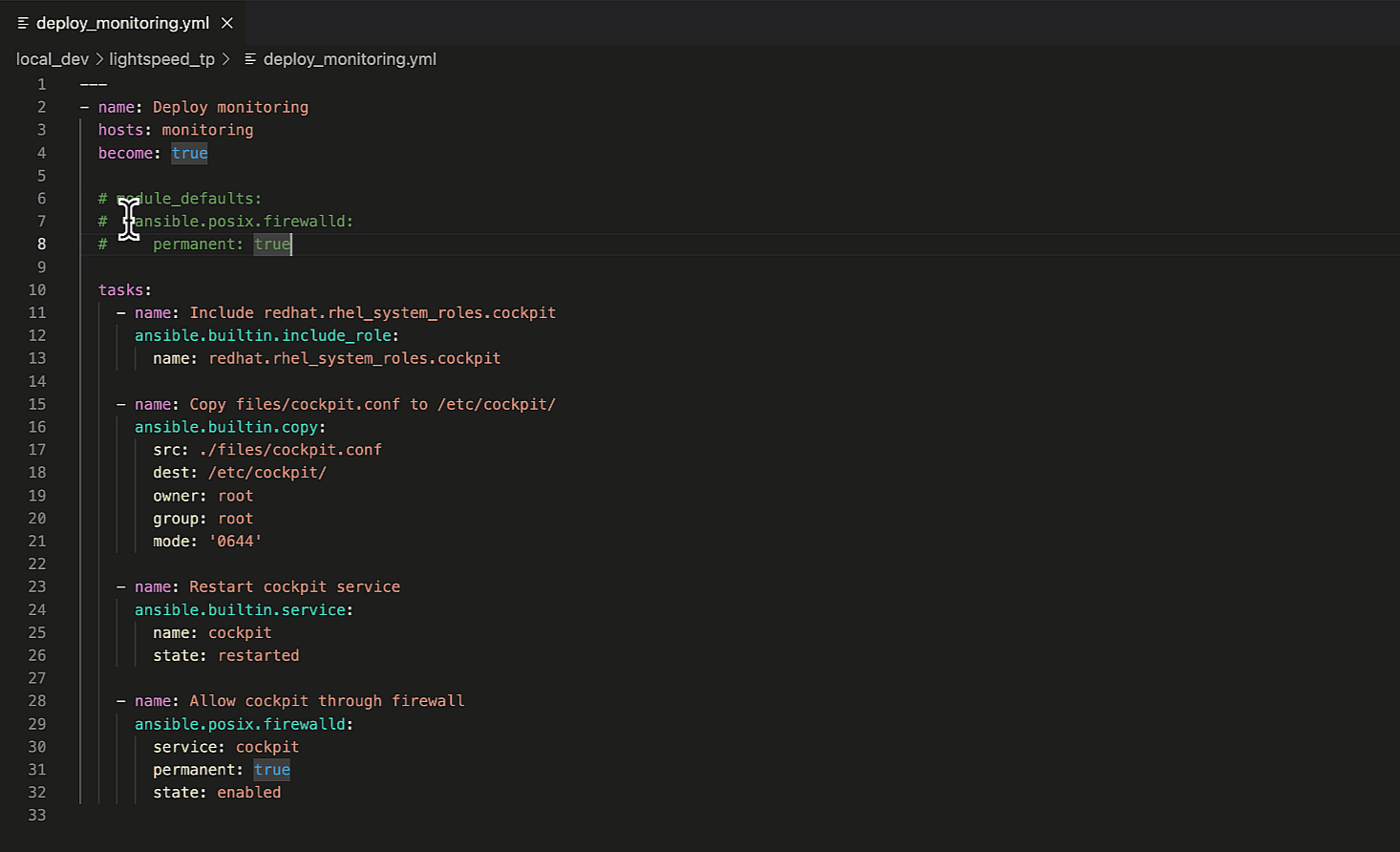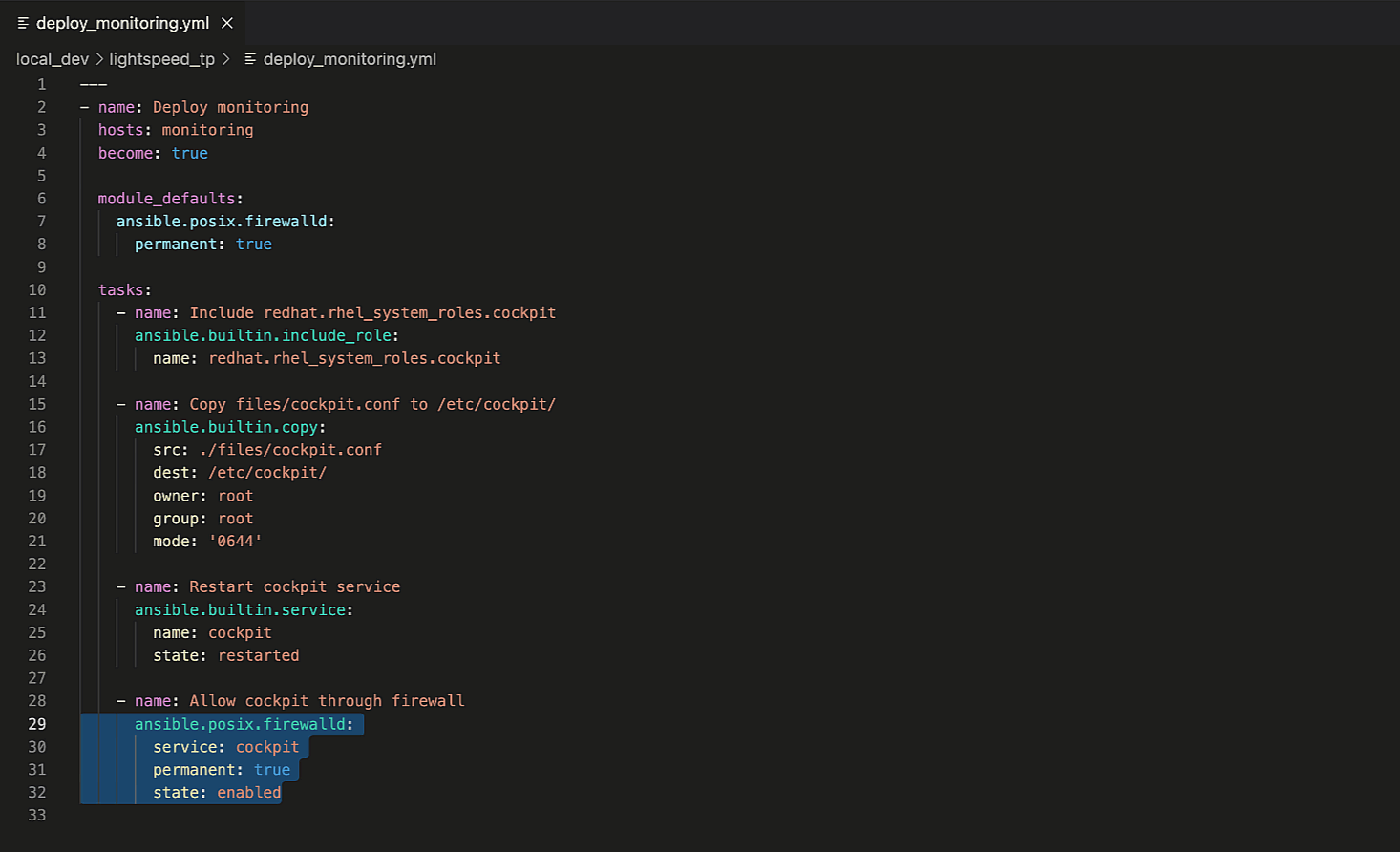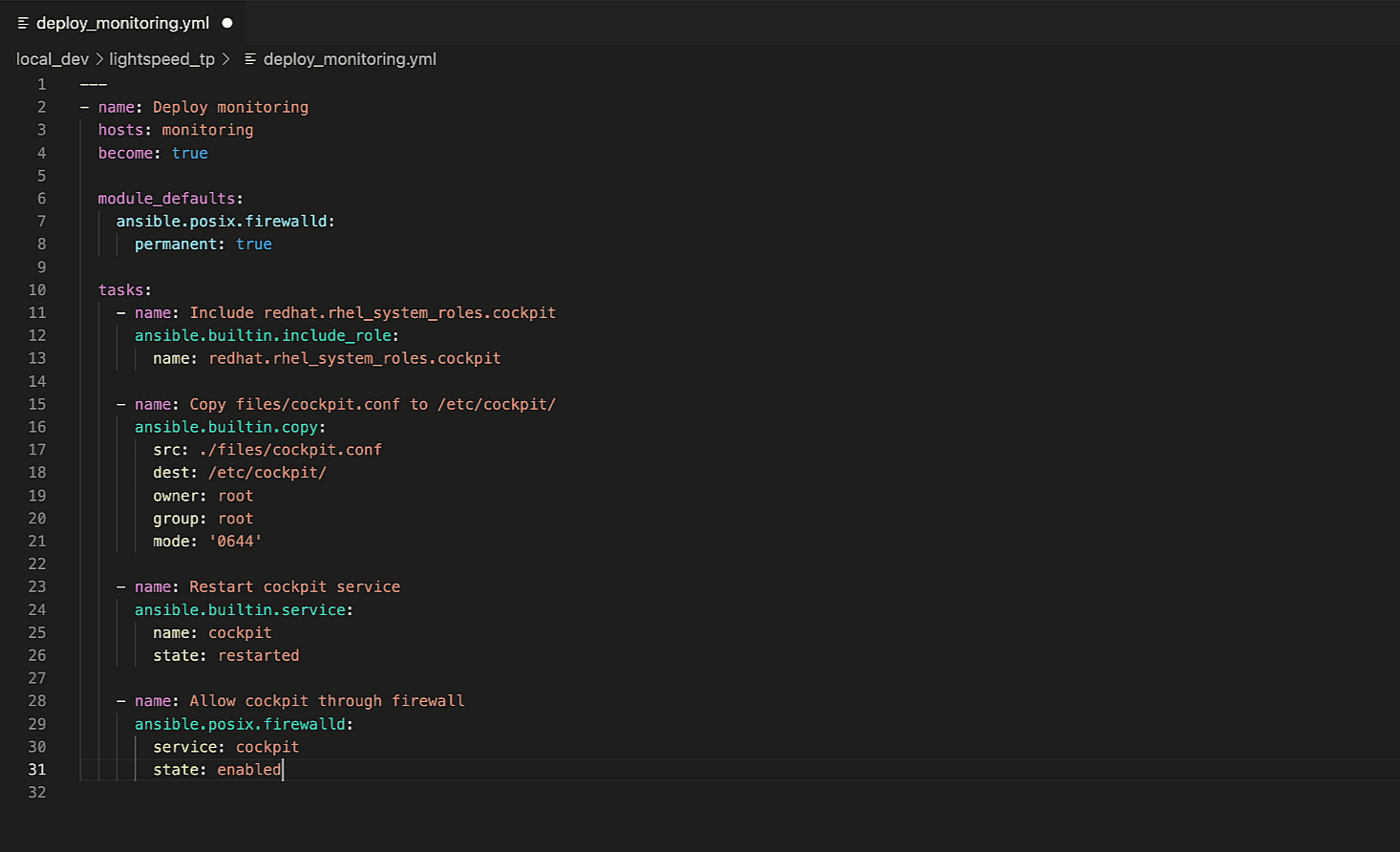
Note that it used the full Playbook context and provided a revised
recommendation that excludes “permanent: true“. You can also apply
this to other Playbook keywords, such as “vars“.
Transparency and openness. Ansible Lightspeed Content Source Matching
Last, and certainly not least, is Ansible Lightspeed Content Source
Matching.
Ansible Lightspeed Content Source Matching.
We transparently share the potential source, Author, and content license
of the training data used for the recommendation. Building trust in the
community and supporting the relationships between authors and
contributors is part of Red Hat’s DNA. These suggestions came from the
Ansible community; we don’t want to hide that.
Wrap-up
Congratulations! You have successfully configured Ansible Lightspeed in
VS Code and experienced its generative AI capabilities with just a few
simple steps.
We encourage you to share your feedback on the technical preview
experience and stay updated on the project by joining the
Ansible Lightspeed Matrix room
to ask questions and get the latest news. Please also
visit the Ansible Lightspeed landing page.
We’ll update you with new resources to help you get the most out of your
Ansible Lightspeed with Watson Code Assistant experience.
Happy automating…with AI!